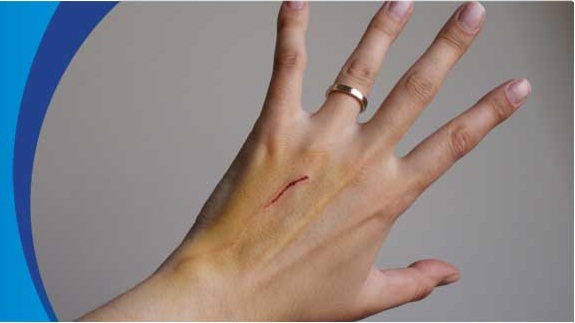
 Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused when bacteria enter our body through a wound that breaks the skin. Some kinds of wounds and skin breaks which are exposed to dirt or saliva or feces are more susceptible to tetanus than other kinds of injuries. The chances of tetanus are also much more if the injury is caused by an object like a needle or a nail that pierces the skin or if the injured tissues become dead. Tetanus affects the body’s nervous system in which muscles become stiff.
Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused when bacteria enter our body through a wound that breaks the skin. Some kinds of wounds and skin breaks which are exposed to dirt or saliva or feces are more susceptible to tetanus than other kinds of injuries. The chances of tetanus are also much more if the injury is caused by an object like a needle or a nail that pierces the skin or if the injured tissues become dead. Tetanus affects the body’s nervous system in which muscles become stiff.
Tetanus is a critical bacterial infection and if not properly treated, the infection can result in death. The infection starts by affecting the neck and jaw muscles making them tight and stiff, which is why it is known as lockjaw. The infection does not limit itself to the neck and jaw muscles and spreads to other body parts and can also impact body’s ability to breathe.
Tetanus Symptoms
There is no definite answer as to when the signs and symptoms of tetanus would show up after the tetanus bacteria enter your body because of a wound. Though not sure, the average incubation period is about seven to eight days for the tetanus symptoms to present themselves.
|
Symptoms |
Description |
|
Initial symptoms |
The initial symptoms of tetanus include irritable and sore muscles. Muscles also get stiff and become cramped and body starts to feel tired. Swallowing food also becomes a problem. |
|
Effects on facial muscles |
The first muscles affected by the infection are the facial muscles. Smile becomes cynical and grim because facial and jaw muscles get cramped. |
|
Results of muscle spasm and cramping |
The muscle spasm is gradual and ongoing and causes the back to arch. The cramping of the muscles can be severe enough to cause the bones and joints to break or dislocate. |
|
Effects on breathing muscle |
Muscles that are responsible for breathing can also get affected at some stage and if this starts to happen the results can be fatal if medical help is not at hand. |
|
Cephalic tetanus symptoms |
Weakness of an additional facial muscle in addition to the jaw indicates cephalic tetanus. In almost 66 percent of cephalic tetanus patients, tetanus progresses to become generalized. |
|
Localized tetanus symptoms |
In case the muscles affected by spasm and cramping are near the location of injury, the tetanus is called localized tetanus. Localized tetanus patients can develop generalized tetanus symptoms as well. |
|
Neonatal tetanus symptoms |
In case the generalized tetanus affects new born babies, the tetanus is referred to as neonatal tetanus. The new born baby has poor swallowing and sucking capabilities if he/she is affected by tetanus. |
|
Other tetanus symptoms |
Other symptoms that are associated with tetanus are high temperature more than 100.4 oF, hypertension i.e. a high blood pressure, excessive sweating and tachycardia i.e. a faster than usual heartbeat. Seizures also sometimes occur in patients with tetanus. |
Risk Factors for Tetanus
The risk of tetanus increases in patients who have a certain existing pre conditions. These factors are:
- The first and foremost reason for tetanus developing patients is a lack of immunity against tetanus. If a person does not receive timely tetanus immunization booster shots immediately after an injury, his/her chances of getting tetanus increase.
- Tissue injury.
- An injury in which skin becomes open and tetanus bacteria enter the site of wound.
- Injury caused by a foreign object like a splinter or a nail.
- The presence of other infection causing bacteria in the body or at the wound site.
- The risk of tetanus also increases if the injured area is surrounded by swelling.
The following kinds of wounds have been known to be susceptible to cause tetanus infection:
- A cut caused by an injection needle, tattoo or body piercing.
- Wounds because of a gunshot, surgery or animal bite.
- An injury caused by a compound fracture, getting crushed or burned.
- Infection in the ear or a foot ulcer that has become infected.
- Infected umbilical stumps of a new born baby born of inadequately immunized mother.
How to Prevent Tetanus
In order to avoid getting infected by tetanus, ensure that you get a tetanus immunization booster shoot immediately in case you get a wound that is deep or the skin gets punctured because of the injury. Injuries caused by an animal biting also leave you open to tetanus and therefore you must receive tetanus toxoid vaccine if you get such an injury. Leave such wounds open until you get medical help. The physician would clean the wound and recommend antibiotics in addition to immunization. If you have already been immunized for tetanus, then antibodies against tetanus would immediately be formed by your body to fight the bacteria.
|
Remedies |
Description |
|
Control bleeding |
Apply pressure on the injury in case of bleeding to stop the wound from continuing to bleed. |
|
Clean the wound |
The wound should be cleaned with saline solution or with clean water after the wound stops to bleed. Also clean the area around the wound with soap. You must visit your physician in case some dirt gets attached to the wound. |
|
Apply an antibiotic |
In order to avoid bacteria to enter the wound, apply an antibiotic ointment like Polysporin or Neosporin. The antibiotic cream does not aid quick healing rather they make the wound heal in an organized way. In case the cream causes a rash, stop the use of the cream. |
|
Protect the wound |
Though for healing, keeping the wound open is better, but from the point of view of infection, it is better to keep the wound clean and covered until a scab forms. |
|
Keep dressing clean |
Keep changing the dressing every day or as soon as it becomes dirty or wet to prevent infection. |
|
Get the tetanus vaccination |
A tetanus immunization shot eliminates the possibility of getting a tetanus infection. Almost every case of tetanus has been recorded in people who had not received a booster shot against tetanus in the prior 10 years. |
When Do I Need a Tetanus Shot?
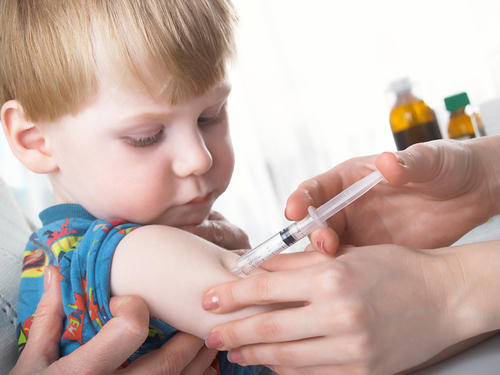 The first thing that you need to consider before deciding whether you need the tetanus shot or not is to ascertain whether the object that caused the injury was dirty or clean. A dirty object is one which has either of dirt or soil, feces or spit on it. Now you will need the tetanus shot if:
The first thing that you need to consider before deciding whether you need the tetanus shot or not is to ascertain whether the object that caused the injury was dirty or clean. A dirty object is one which has either of dirt or soil, feces or spit on it. Now you will need the tetanus shot if:
- You had your last immunity shot 10 years ago and the object that caused the injury was clean.
- You had your last shot 5 years ago and the object causing the wound was dirty or you cannot decide if it was dirty or clean.
- You are uncertain of the time since your last shot.
- You are yet to receive the primary vaccination series for tetanus.
The following video tells you more about the tetanus: