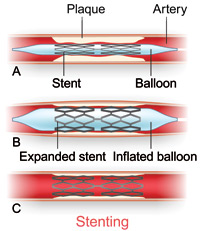
Narrowed arteries can cause a person to feel chest pain and eventually lead to a heart attack. When this happens, a person has to have an angioplasty. During an angioplasty, most patients receive a stent which is an expandable little tube. The stent is put into the artery in order to help treat an artery that is weak or has become narrow. Those who do not have a stent implanted during surgery are at a 35% to 40 % chance of having their arteries close within six months, which is known as restenosis. Those who do have a stent placed into the artery reduce their chances of restenosis by around 20%. When one is dealing with artery issues, a heart stent can save life.
Why Is a Heart Stint Needed?
1. To Treat Narrowed Arteries
There are times in which plaque builds up within the arteries, causing these arteries to become narrower. When this happens, the blood flow to the heart is greatly reduced which means organs and the brain are not getting the necessary oxygen rich blood in order to function. This can put a person at risk for a heart attack or stroke. With heart stents inserted into the artery, the artery can be widened to help increase the flow of blood throughout the body.
2. To Prevent a Burst in the Aorta
The aorta carries blood from the left side of the heart to the entire body. In many cases, the aorta can become weakened over time which can cause an aneurysm which usually occurs in the abdomen and can burst causing severe internal bleeding. When this happens, the stent is placed into the aorta in order to help strengthen the wall and prevent the aneurysm from bursting, while also helping to promote blood circulation.
3. To Remove Aortic Tears
When a tear occurs in the aorta,it can lead to blood loss throughout the body, which results in the organs not getting the necessary blood for proper function. Usually it happens in the chest and can result in chest pain or even a heart attack if left without care. To combat this, a stent is placed where the tear is within the inner wall; in turn this helps to strengthen the aorta and allows blood flow to get through the artery.
Benefits and Risks of Having Heart Stent Surgery
1. Benefits of Having Heart Stent
The main benefit of heart stent surgery is that this can save your life and also increase the quality of life.
- Those who have this surgery often see immediate results, as they feel better since they are now getting the proper amount of blood flowing into the body.
- Compared to open heart surgery to fix such problems, stent surgery is much less evasive and has a faster healing time. Most patients are discharged within 12 to 24 hours and recover fully within a few weeks, while open heart surgery may require a hospital stay of up to a week and months of recovery. Those who have stent surgery are usually back to their daily activities within a week or so, and find that activities that were once difficult, become much easier and that pain is lessened in the chest area. The amount of time for recovery depends upon the person and the degree to which they have heart issues.
2. Risks of Having a Heart Stent
There are some risks associated with a heart stent surgery, though most are not as risky as not having anything performed when there is a heart issue. These risks include:
- Restenosis: Those who do not have a stent in place will find that they have a 30% chance of having further heart issues. For those who do use a stent, the risk reduces. However, there is still a small percentage about 10%-20% that one will have further heart trouble.
- Blood clotting: Even though a stent is meant to help the artery, there is a chance that a blood clot can form within the stent. When this happens a person can have a heart attack. In an effort to prevent this, doctors recommend taking aspirin or blood thinners to keep the blood from clotting because they keeps the blood thin and easy to go through the arteries.
- Bleeding: When a stent is inserted, the catheter may go in through the arm or the leg. There is a chance that the insertion site can bleed which usually results in a bruise. However, in a few cases, this can lead to excessive bleeding that need to get a transfusion and repair whatever is causing this excessive bleeding.
- Kidney problems: There is a special dye that is used during the process that can cause kidney damage. However, this usually only happens in those who already have damaged kidneys. Steps are taken to prevent this such as using less dye or ensuring a person is well hydrated before the operation to flush the dye as fast as possible.
- Stroke: There is a chance that blood clots or plague can break lose. Although rare, the clots maygo towards the brain during the operation. If so, it can result in a stroke while under anesthesia. Doctors give blood thinners during operations in order to prevent this from happening.
- Others risks: During the procedure, there are other risks that can happen, including:
– Risks of having a heart attack;
– The coronary arteries can become damaged and results in immediate bypass surgery to correct the issue and save the person from having a heart attack or dying;
– The heart can beat too fast or too slow during the operation. However, this is usually short lived and does not result in permanent issues.