Skin covers the bones, muscles, tissues and organs and its primary operation is to safeguard the body’s internal organs from infection. Bacteria, germs and viruses are the main sources of skin infections, which in some cases can also escalate to cause infection beyond the skin by entering into the bloodstream. The symptoms of infections differ a lot in the degree of severity and intensity.
Viral Skin Infection
A skin infection can be caused by a lot of different viruses, and such infections can range in both severity and effect. Some viral skin infections are also related to systemic diseases. A few of the more common and primary skin infections are explained below.
1. Chickenpox
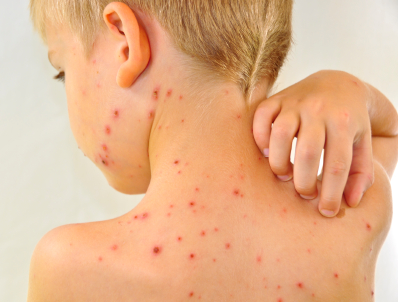 Chicken pox (varicella) is a viral skin infection which also incorporates symptoms like headache, fatigue, discomfort, fever and a lack of appetite. The effect of the virus on the skin is an itchy rash which appears more like a blister. This viral skin infection can spread to people who are neither vaccinated for the disease nor have caught the disease previously.
Chicken pox (varicella) is a viral skin infection which also incorporates symptoms like headache, fatigue, discomfort, fever and a lack of appetite. The effect of the virus on the skin is an itchy rash which appears more like a blister. This viral skin infection can spread to people who are neither vaccinated for the disease nor have caught the disease previously.
Treatments: Doctors may suggest an antihistamine to reduce the itchy feeling and allow the virus to complete its time. It is strictly advised to avoid scratching because it would only slow down the process of healing in addition to making the sores susceptible to infection. In order to relieve the itchiness, patient can use calamine lotion on the sores and take a bath by adding baking soda, uncooked or colloidal oatmeal to the water, both of which aid in soaking.
2. Shingles
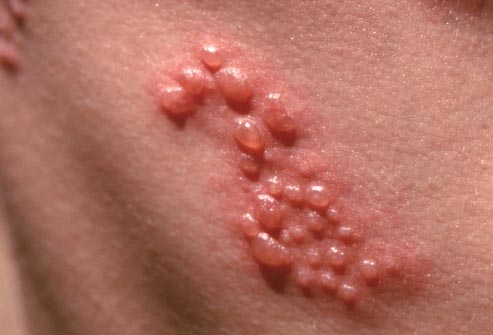 Shingles is a viral infection that can manifest itself in the shape of continuous blisters on either side of the torso. Rashes and blisters caused by this viral infection are very painful. Signs and symptoms of shingles start with a burning pain or numbness. The pain is followed by a stripe of red blisters which are filled with fluids and can burst open. Itching is also a constant symptom of shingles.
Shingles is a viral infection that can manifest itself in the shape of continuous blisters on either side of the torso. Rashes and blisters caused by this viral infection are very painful. Signs and symptoms of shingles start with a burning pain or numbness. The pain is followed by a stripe of red blisters which are filled with fluids and can burst open. Itching is also a constant symptom of shingles.
Treatments: Shingles has no cure and taking a bath and pressing the blisters with cool things can reduce the discomfort caused by pain and itching. Antiviral drugs, if taken immediately after first signs of shingles present themselves, increase the chances of a quick healing.
The following video tells you more about viral skin infection:
Bacterial Skin Infection
Presence of bacteria on human skin is common and they do not cause much harm to the skin. However, a few bacteria can enter the skin because of a wound or a cut and cause skin infections. Swelling, redness, pus and pain are the general symptoms of the skin infection caused by bacteria.
1. Impetigo
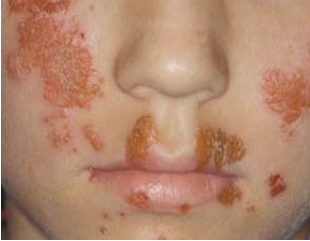 Impetigo spreads by physical contact with a person who has the infection or by using towels, clothes or objects used by the infected person. The infection only starts as blisters that reveal the moist red skin, but later develops into a golden crust with a grainy texture.
Impetigo spreads by physical contact with a person who has the infection or by using towels, clothes or objects used by the infected person. The infection only starts as blisters that reveal the moist red skin, but later develops into a golden crust with a grainy texture.
Treatments: The impetigo infection generally disappears within 2-3 weeks; but because the disease is contagious, it is advised to get a treatment for the disease to reduce chances of spreading the disease as well as to stop it from becoming severe. The general treatment recommended for this infection is the application of antibiotic cream on the blister patches. In order to let the cream penetrate into the skin, the crusts should be cleared with soap water before applying it.
2. MRSA
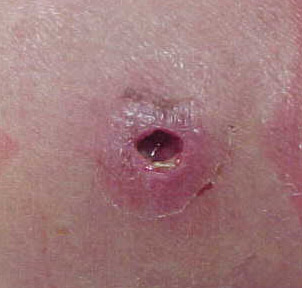 MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) starts as red pimples, which are more like boils or spider bites. These red pimples can become swollen and deep in no time, requiring to be drained by surgery.
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) starts as red pimples, which are more like boils or spider bites. These red pimples can become swollen and deep in no time, requiring to be drained by surgery.
Treatments: Antibiotic is a treatment for the bacterial infection and must be taken till your physician asks you to stop taking it. If you do not complete the dose of antibiotic, some bacteria might continue to exist and the infection might continue. In some cases, doctors can also call for surgery to drain the boils on your skin.
3. Other Types of Bacterial Skin Infection
- Leprosy is a bacterial skin infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae and the infection can stay quiet and show no symptoms for a long time. Common symptoms include granulomas of the respiratory tract, eyes etc. It can be treated through the use of antibiotics.
- Carbuncles are a collection of boils that are interconnected below the skin and show up in the form of an abscess with a single or multiple openings that push pus out onto the skin. The pus needs to be drained first in order to treat it and contacting a doctor is the best choice if the abscess persists for a certain time.
- Boils are infections of hair follicles which show themselves in the form of swollen areas. They are accompanied by redness and pus. While they need no real treatment in most cases, a boil should be drained and kept clean to avoid complications.
- Staph infection and Cellulitis. Staph infection is usually caused by the bacteria known as Staphylococcus (better known as Staph). Staph usually affects the foot, the nose or the genitals. A staph infection that affects the skin is known as Cellulitis. The infection is usually treatable with the use of antibiotics.
Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections are caused by fungi and they are usually found in parts of the body that are often moist and wet. The space between each toe, the genitals and the surrounding area, the breasts and the area under them are places where fungi usually create their home. They can spread to other areas of the body as they reproduce through the release of spores which can move around either through contact or through inhalation. The fungi remain dangerous for this reason as they can end up affecting the skin, resulting in penetration to major body organs causing a systemic infection in the entire body. On a slightly lesser scale, fungi can cause lung, nail and skin infection.
1. Athlete’s Foot
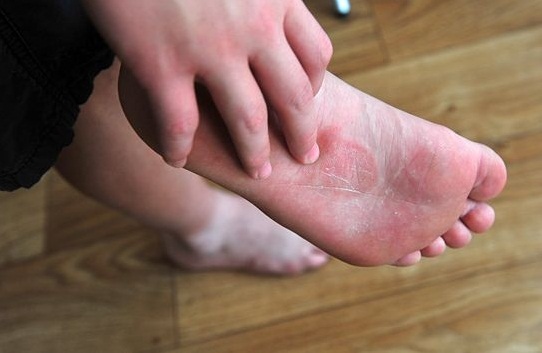 Athlete’s foot is caused by the fungi as they love to reside in moist and wet environments like the swimming pools, the public shower flooring and socks. Athlete’s foot usually shows itself in the form of red burning and itchy spots, while it might show up in the form of a sore or blister too in some cases.
Athlete’s foot is caused by the fungi as they love to reside in moist and wet environments like the swimming pools, the public shower flooring and socks. Athlete’s foot usually shows itself in the form of red burning and itchy spots, while it might show up in the form of a sore or blister too in some cases.
Treatments: The treatment option mostly used for Athlete’s foot is antifungal topical medication. However, in the most serious of cases, the doctors might prescribe oral drugs.
2. Ringworm
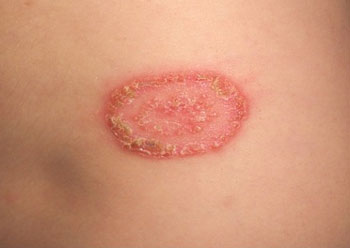 Ringworm is another common fungal infection which shows up in the form of a rash that is reddish and very itch initially and becomes a kind of a large red ring over time.
Ringworm is another common fungal infection which shows up in the form of a rash that is reddish and very itch initially and becomes a kind of a large red ring over time.
Treatment: Since fungi love wet and moist environments, it’s best to keep the area dry as much as possible. The best treatment for ringworm is to dry the area where the infection lies and then use a topical antifungal cream.
Please watch a video for more information about fungal skin infections: