Molluscum contagiosum is a fairly common viral infection of skin. The infection is frequently reported in children and young adults, especially in the first 10 years of their lives. Although anyone can develop this infection; yet children with compromised immune systems (such as patients of AIDS and SLE) are more vulnerable. Researches have shown that this virus manifests gender predisposition with a much higher number of male cases as compared to females. Statistically, tropical regions are at high risk of this infection. The overall prevalence within United States is 1% of all dermatological conditions reported in clinical setting.
Causes of Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
The causative agent of this infection is Molluscum Contagiosum virus or simply MCV. There are 4 identified strains of this virus, of which, type 1 is found most common in causing this infection and interestingly, this virus only affects humans. After primary exposure to this virus, the replication phase of this virus begins, which shortly leads to symptoms. Symptoms can start to appear between 2 weeks to 6 months of exposure, depending upon the strain and baseline immune condition of the affected body. For children have a relatively weak immune system, they are more vulnerable.
Symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
After exposure to the virus, the first 2 to 6 weeks are essential in identifying the symptoms in order to confirm diagnosis. Here is a list of the typical symptoms associated with the disease:
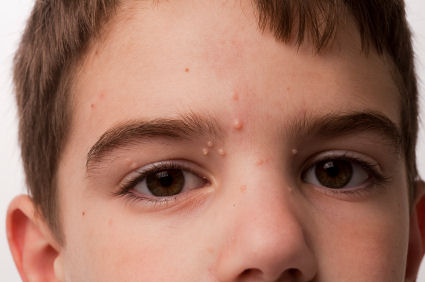
- Collection of swollen and embossed lesions. They are likely to occur in a collection of 5 to 15 in number;
- Shiny, lustrous and smooth looking papules;
- The lesions have a depression in the center and are often slightly red or pink color, as if they were a continuation of the flesh;
- Children usually have the lesions in the torsi, abdomen, face and limbs, in both adults and children, the palms and soles are usually spared;
- The size varies between 2mm to 6 mm, and they are mostly filled with waxy depositions.
It is important that parents should know that the lesions are not painful, but they are itchy in nature. If parents suspect their child have the virus, they should take their baby to a dermatologist.
Treatments for Molluscum Contagiosum
Viral conditions can be very tricky to treat, but with Molluscum Contagiosum home remedies are one of the easiest and very effective treating methods. However, it is necessary that the treatment being used be confirmed by the doctor.
1. Home Remedies for Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
Here are 2 useful home remedies for dealing with molluscum contagiosum:
- Try homemade lotion
Using natural, antiseptic products such as tea tree oil, cider vinegar and elderberry extracts can help eliminate the virus gradually. They should be applies locally to the affected areas.
- Bursting the lesions
In some cases, moms resort to bursting the lesions with the application of gentle pressure. This has proven effective for many individuals, but proper care needs to be taken with cleaning the areas and not letting the waxy liquid spread to other part of the skin. Moms who are willing to try this method should burst the lesions with clean, ideally sterile hands.
In large lesions, it is generally recommended to use peroxide to clean the skin. After thorough washing with water, a local antiseptic such as Neosporin can be applied locally. Compared to months of treatment, this treatment can alleviate the lesions within a few weeks.
2. Medications for Molluscum Contagiosum
Allopathic treatments mainly focus on the use of drugs that can treat the symptoms of the disease. Topical creams and lotions of the following drugs are available and have proven effective in treating the lesions.
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Potassium hydroxide
- Salicylic acid
- Trichloracetic acid
Prevention of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum Contagiosum virus results in the formation of clusters of lesions that are fleshy looking and embossed.
1. Transmission Route of Molluscum Contagiosum
Transmission is usually through skin-to-skin route. If you scratch the lesions and then touch the unaffected body parts with the same finger, lesions will start to appear on that part.
Besides, sexual contact and touching contaminated clothing and bedding can also result in the spread of virus.
For kids, the interactions in day care can greatly spread this virus around.
2. Precautions of Molluscum Contagiosum in Children
- Since the spread of this virus is mainly from contact, one needs to avoid sharing of towels, clothes and replace beddings every day;
- In addition, bandages are used to cover the lesions in order to prevent exposure and allow quick healing. If a child is going to exposure to water, he needs to cover the lesions with water resistant bandages and keep away from sharing towels;
- Wash babies' hands with an antiseptic soap;
- Don't use unclean hands to touch lesions;
- Avoid using a razor in areas where lesions are present.
You may watch the video below to learn about molluscum contagiosum as well as the corresponding treatments for molluscum contagiosum in children: