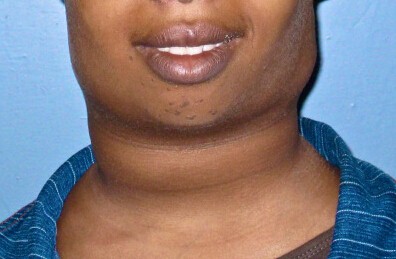
 The picture on the right shows a patient who is infected with Hodgkin Disease. Take note of the neck and the lower side of the cheeks—they’re swollen. This is one of the most obvious Hodgkin's disease symptoms.
The picture on the right shows a patient who is infected with Hodgkin Disease. Take note of the neck and the lower side of the cheeks—they’re swollen. This is one of the most obvious Hodgkin's disease symptoms.
Hodgkin’s disease, also known as HD, Hodgkin disease, Hodgkin lymphoma or Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a type of cancer called lymphoma. The disease was discovered by Doctor Thomas Hodgkin, which explains its name. The cancer originates from disease-fighting cells known as lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. The disease can occur at any stage in life, but mostly from the age of 15 and 40. HD mostly emerges from the chest, neck and underarms lymph nodes.
Hodgkin's Disease Symptoms
There are different types of Hodgkin’s disease. The different kinds of Hodgkin's disease symptoms are classified according to their appearance under the micro-scope.HD can be classified into two types:
- Classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: It’s made up of mixed cellularity and nodular sclerosis.
- Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s disease: This type affects 5% of patients
The two types of HD are cancerous because their growth invades and destroys tissues and cells. Symptoms may include:
- Swelling of lymph nodes in your neck, groin, and armpits. The swellings are painless.
- Perpetual fatigue
- Fevers and chills
- Sweating a lot at night
- Weight loss
- No appetite
- Itching continuously
- Lymph node pains after drinking alcohol
A patient shares more information on symptoms of Hodgkin's Lymphoma through her own experience:
Tests Used to Diagnose Hodgkin's Disease
If you notice Hodgkin's disease symptoms, you should see your doctor and run some tests.
|
Tests |
Description |
|
Physical exam |
The doctor monitors for swollen lymph nodes in your neck, underarm and groin, and also the condition of your spleen and liver. |
|
Blood test |
The doctor takes a sample of your blood to check for indications and possibilities of cancer. |
|
Imaging tests |
Imaging tests are tests like computerized tomography scan, emission tomography and X-rays.You will go through one of the tests or even all, at times, for monitoring of your cancer condition. |
|
Removal of swollen lymph node |
Your surgeon will remove a part of your swollen lymph node and do a lab test for any signs of HD. |
|
Bone marrow testing |
Removing bone marrow is very delicate procedure. Your doctor will remove a sample of bone marrow, blood and bone using a small needle. Then a biopsy will be carried out. |
Stages of Hodgkin's Disease
After the diagnosis has been done, the cancer is then staged. Staging refers to describing the location and spread of the disease. The stages include:
- Stage I (early Stage): Cancer is located in one lymph region
- Stage II (locally advanced disease): Cancer is located in two lymph regions, on one side of the diaphragm, on the other side it’s found near the area organ.
- Stage III (advanced Disease): Cancer is located in lymph node areas both above and below the diaphragm.
- Stage IV (widespread disease): Cancer is located outside the lymph nodes and spleen. The cancer has spread to many areas such as the bone, bone marrow and the skin.
Treatments for Hodgkin's Disease
- Radiation therapy, chemotherapy or combined therapies: These are the main therapies carried out to monitor HD. At times, these (chemotherapy and radiation therapy) therapies turn out to be dangerous in that they increase the risk of developing secondary solid tumors.
- Targeted therapy: This is mostly carried in people with lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. The therapy is directly engraved into your vein via a thin needle. The drug might cause vomiting, diarrhea, excessive night sweats, nausea and tingling hands or feet in some cases. These effects will end after treatment is over.
- Vaccinations: People with Hodgkin’s lymphoma should be administered with polyvalent pneumococcal vaccine and influenza. Patients with asplenia or splenic dysfunction are administered with haemophilus influenza type B and Meningococcal group C.
- Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: The role of this treatment is still being explored.
Follow-up Care After Treatment
Cancer treatment may arouse other cancer types. You should go for follow up checkups after your treatment. Exposure of your chest to radiation rays may expose you to breast cancer, lung cancer and heart cancer. This may turn out to be more dangerous for you. Furthermore, you can talk to your doctor if you are having long term effects. This will help you reduce the risk of upcoming issues. You can also join a support group and make good friends. Having good friends who you trust will help you open up to them by telling them what your health situation is and also sharing with them how you feel. It’s better to have a wall where you can lean on rather than keeping all your issues to yourself. Support groups may also help you raise money for your treatment
Preventing Infection After Cancer Treatment
Chemotherapy and stem cell transplants increase your risk for infections. You must be very careful and avoid germs. Here are some ways how you can prevent infections.
- Have a good lifestyle, which is supplemented with good hygiene. Wash your hands regularly and brush your teeth after every meal. Keep your personal compound clean.
- Keep off crowded places especially during flu and cold times.
- Eat well cooked foods. It’s advisable that you make your own meals at home and avoid buying fast foods. Avoid raw fruits also.
- Always boil your drinking water before using it. This will kill the microscopic organisms that are found in water.
- Avoid decorating your house with fresh plants and flowers. Most plants carry molds, which can cause infections.