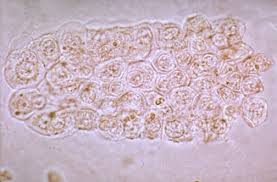
 The epithelia cells are simply cells that are gotten from the epithelium, which is the lining found in and outside the body. These cells are produced often, and old cells shed away to give room for the new cells. Different parts of the human body have distinctive epithelial cells. Sometimes epithelial cells in urine can happen and their presence can offer information that can be of diagnostic use. This greatly depends on the type of epithelial cells and the number present. By spinning the urine to separate sediment, it is possible for pathologists to see renal, squamous as well as transitional epithelial cells.
The epithelia cells are simply cells that are gotten from the epithelium, which is the lining found in and outside the body. These cells are produced often, and old cells shed away to give room for the new cells. Different parts of the human body have distinctive epithelial cells. Sometimes epithelial cells in urine can happen and their presence can offer information that can be of diagnostic use. This greatly depends on the type of epithelial cells and the number present. By spinning the urine to separate sediment, it is possible for pathologists to see renal, squamous as well as transitional epithelial cells.
Why Are There Epithelial Cells in Urine?
When tests come out positive for epithelial cells in your urine, it is ideal to learn of the exact type of cells present as well as the concentration. A small concentration of cells is most of the time not a cause of concern. However, if there are high numbers of epithelial in urine, there may be need for new urine samples to be taken to be able to get cleaner urine samples. An increase in the number of these cells may require more tests to be done to be able to ascertain the condition. These additional tests make it possible for physicians to know the exact level as well as the severity of the infection. Following are possible causes for elevated levels of epithelia cells in urine:
1. Natural Sloughing
The presence of epithelial cells in urine can be as a result of normal sloughing of the epithelial tissues and may not necessarily indicate any abnormalities. The ureters, which are responsible for carrying urine from the body, are lined with epithelial tissues. Just like the skin, the epithelial tissues will slough from time to time and are replaced by new cells to keep them functional. The sloughing cells mostly end up in the urine, albeit in minimal amounts. They are then excreted.
2. Indication of Nephrotic Syndrome
According to studies, presence of epithelial cells in large numbers in the urine can indicate a problem with the kidneys. This is more so if the present cells come with attributes that are morphological, which may identify them as cells from the renal tube. Cells from renal tunes are characterized by round shapes and large nuclei which point to nephrotic syndrome. This syndrome occurs as a result of nonspecific damage to the kidneys, which can lead to degeneration of the renal tubes. These renal tubes are responsible for carrying filtered blood to the kidney. The functions of the renal tunes play a big role in the production of urine and hence degenerations of these tubes can be a serious condition.
3. Signs of an Infection
Urinary tract infections can lead to the increase in the number of epithelial cells present in urine. Most UTIs start from the bladder when the E.Coli bacterium makes its way from the urethra to the bladder. Once this bacterium settles in the bladder epithelium, they cause irritation and hence lead to above normal epithelial sloughing. An infection that is left untreated can escalate to the kidneys and thus cause upper urinary tract sloughing.
Other Factors to Be Aware of Concerning Epithelial Cells in Urinalysis
As it had been said earlier in this article, the presence of traces of epithelial cells, more so the transitional and squamous cells, is considered to be a normal occurrence in people. An increased number of squamous cells in urine samples can indicate contaminations of the sample and is mostly common in females.
- Women suffering from vaginal infections caused by bacteria may show large amounts of squamous epithelial cells in their urine. These cells mostly come with bacteria attached and are referred to as clue cells.
- In older women, immature and small epithelial cells from the vagina (parabasal squamous epithelial cells) can be present in urine samples. This is common in post menopause women with low estrogen levels.
- Also, transitional cells found in urine are quite uncommon and mostly found in elderly people. Most of the time, the presence of transitional cells in urine can be as a result of transitional cell cancer of the renal pelvis.
- Tubular cells filled with fat deposits can be present in urine samples for people suffering from lipiduria. These types of cells are referred to as oval fat bodies.
Other Substances That Can Be Present in Urinalysis
Except epithelial cells in urine, other substances can appear in urine, too. Chemical examinations can be undertaken to determine other substances in the human urine. Automated instruments are most ideal when looking for substances in human urine as they help in eliminating discrepancies from human interpretation. A microscopic analysis makes use of a microscope to identify as well as count cells, bacteria, crystals and mucous among other substances. The amount of any substance found in the urine is reported with regards to the microscopic strength used to view the substance -per low power field (LPF) or per high power field (HPF). It can also be reported as an approximate amount like rare, moderate, few or many.
|
Substance |
What Is Noticeable and Why |
|
Red blood cells |
The number of red blood cells in the urine can be as a result of urinary tract or kidney disease, medications, trauma, intense exercise as well as smoking. Also, menstrual flow can cause presence of red blood cells in urine. |
|
Bacteria |
Can be a result of an infection. Also, bacteria on skin can contaminate a urine sample. |
|
White blood cells |
This indicates an inflammation of the urinary tract or kidneys. Can be contaminated by vaginal secretions. |
|
Casts |
Strenuous exercise can cause presence of casts in urine. Casts made from white or red blood cells indicate infections of the kidney. |
|
Crystals |
Can occur in urine when solute concentration, PH and urine temperature reach a specific range. Crystals made with substances not found in urine can indicate an abnormal process or liver disease. |