Many people, especially those who are concerned about anti-aging ingredients, have heard about peptides and their supposedly miraculous results. Claims can include a range of things, such as eliminating puffy eyes and dark circles, lifting saggy skin and plumping lips. With these supposed benefits, it is common to wonder what peptides are and whether they can live up to these claims, such as peptides for muscle growth. The good news is that because they are natural, peptides side effects are very minimal.
What Are Peptides?
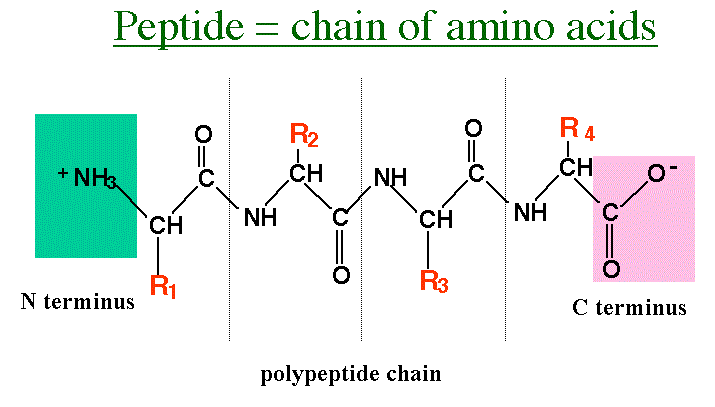
These are biological molecules which occur naturally, which are consisted of small amino acid monomer chains linked together via peptide bonds. These chemical bonds are covalent in nature and form if the amino group from an amino acid has a reaction with the carboxyl group from another one.
Dipeptides are the shortest type of peptides, having only one peptide bond and two amino acids. There are also tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and others. Polypeptides are continuous, unbranched and long peptide chains. This means that all peptides are biological polymers and oligomers, a classification which also includes polysaccharides, oligosaccharides and nucleic acids.
You can tell peptides apart from protein based on their size and a benchmark would be about 50 amino acids or fewer. Proteins have at least one polypeptide that are arranged to be biologically functional. This means they are frequently bound to complex macromolecular assemblies, macromolecules like other proteins, or ligands like cofactors and coenzymes. If you truly want to understand "what are peptides", it is important to remember that the size boundaries separating proteins and polypeptides from peptides aren’t absolute. Insulin, for example, is a smaller protein and has been considered a peptide.
In some cases, amino acids will be part of peptides, in which case they are known as residues. This name comes from a hydrogen ion being released from its amine end, a hydroxyl ion being released from its carboxyl end, or both occurring in the way a water molecule releases when an amide bond is formed. With the exception of cyclic peptides, all peptides contain a C-terminal and N-terminal residue on their ends.
What Are the Functions of Peptides?
Now we have known "what are peptides", let's move on to know more about the functions of peptides.
- One of the major functions of peptides is to work as hormones because these are a specific type of peptide responsible for carrying signals between cells and glands. These peptides will control blood sugar regulation, sleep, and other body functions. They are created by the liver, intestine, stomach, kidneys and endocrine glands. Common peptides found in hormones include oxytocins, gastrins, bradykinins, human growth hormone and insulin.
- The brain produces neuropeptides, which you find in neural tissue. They are an extension of your neurosystem throughout your body, meaning that they act as regulators and signals in various processes triggered from locations within the brain. One example of neuropeptides would be endorphins.
- Alkaloids are another type of peptide and they are commonly involved in developing defense mechanisms in small animals, plants and fungi. Examples of these peptides include dynorphin, pandamine and ergotamine.
- When peptides work as antibiotics, they prevent microorganisms from growing within the body. This is an example of using peptides side effects to kill bacteria that cause diseases as antibiotics are commonly used in medicine.
- Peptide can help support our body. This is because when peptide chains become long enough, it will form proteins, which are used as building blocks of animal and human bodies. Keratin is a perfect example as this protein is in human nails and hair and animal claws, hooves, scales, feathers and horns. Collagen is another protein created from peptides and is found in bones, tooth enamel, ligaments and tendons.
How Can Peptides Benefit Our Body?
Now that you have answered "what are peptides", it is time to learn about their benefits. Specific benefits will vary based on the type of peptide in question.
- You can use peptides for muscle growth, and this is one of the most common reasons they are used. Peptides will create an anabolic effect on an athlete's muscle mass, helping them when they suffer a muscle injury. Peptides can quickly heal any damaged muscle fibers, allowing the athlete to return to fields more quickly. They can also help bodybuilders build muscle mass faster than normal, giving them a significant decrease in body fat and a corresponding increase in muscle mass. Peptides are preferred over other mass-building methods, such as steroids because there are almost no peptides side effects compared with the damaging side effects of steroids.
- Pentapeptides, for example, contain five peptides which are connected. These will stimulate hyaluronic acid and collagen, both of which are naturally found in the skin, but decrease in quantity as we age. As these components support skin structure, you develop sagging skin and wrinkles when they decrease. Beauty products aim to counteract and stop this damage with pentapeptides.
- Oligopeptides have six, seven, or more peptide units and they may be referred to using specific names such as heptapentides (a chain of seven peptide units). Oligopeptides will also stimulate hyaluronic acid and collagen production.
- Copper peptides connect with copper molecules to perform their function. This combination of molecules will then travel into the skin's deep layers, where they promote skin healing and collagen production. Copper peptides are typically small molecules since they attach themselves to copper molecules and then drag them through multiple layers of skin.
- Neuropeptides provide benefits by affecting the neurotransmitters within the skin. During the communication of neuropeptides, the nerve cells within the skin will stop communicating with each other but relaxinstead. This allows the skin to become smoother and wrinkles to disappear.